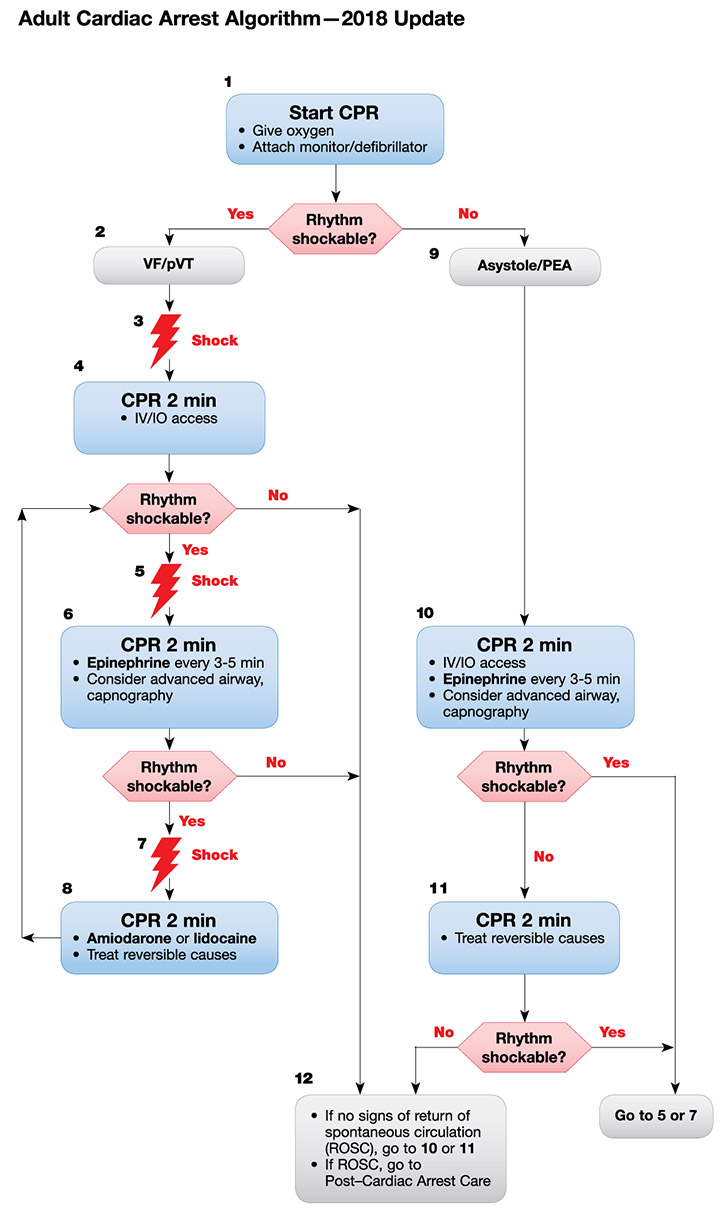
Pulseless Arrest :: CPR q 2 min ::
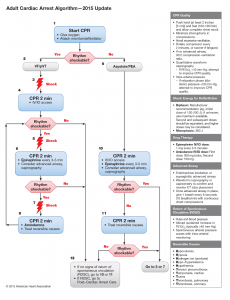
VF, pVT > defibrillator 150-200 J ประเมิน q 2 min
- — after 2 min แรก : Epinephrine 1 mg IV q 4 min, ETT, ‘
- — after Epi (Refractory) > Amiodarone 300 mg IV > 150 mg IV /3ml
Torsade de point (Polymorphic VT) > defib 150-200 J + MgSO2 2 gm IV
>>> MgSO4 1-2 gm + D5W 10 ml IV
- — ห้ามใช้ amiodarone
- — ให้ lidocaine 1 mg/kg > 2% 20 (10%) mg/mL
+ CBC, BUN, Cr, E’lyte, Ca, Mg, P
+ DTX
+ EKG 12 leads
+ ABG
+ หา cause of arrest
- 5 H: Hypovolumia (IV load), Hypoxia (ETT), Hydrogen (7.5%NaHCO3), Hypo/HyperK, Hypothermia
- 5 T: Tension pneumothorax/temponade of heart (ฟัง), Toxins, Thrombosis pulmonary(PE), coronary(MI)
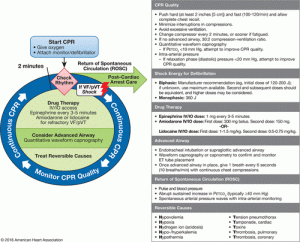
# Tachycardia (>150)
ABC
Stable:
—- IV, EKG 12 lead
- > Adenosine (narrow regular) 6 mg double syringe IV push > 12 mg
- > Antiarrthythmic (wide QRS) : Amiodarone 150 mg+ 5%DW 100 ml IV drip in 10 min
then maintain 1 mg/min for 6 hrs **ห้ามให้ใน QT prolong, Torsade de pointes
Unstable:
BP drop, AOC, shock, ischemia chest pain, AHF
—- sedation, Synchronized cardioverion
- > Narrow: regular(SVT) 50-100 J / irregular(AF) 120-200 J
- > Wide: regular(VT) 100 J / irregular defib.
# Bradycardia (<60)
- 1st degree AV block : PR prolong (> 0.20 sec)
- 2nd degree AV block : Morbitz I > PR prolong progressively + Block, Morbitz II > regular PR + Block
- 3rd degree AV block : AV dissociateion
Stable:
Monitor & Observe
Unstable:
- – Atropine 0.6 mg IV q 3-5, MAX 3 mg (5 doses)
- + Transcutaneous pacing
- – Dopamine 2-20 mcg/kg/min
- – Epinephrine/Adrenaline 2-10 mcg/min
ยาที่ให้ทาง ETT = LEAN (2-2.5X IV dose > MSS flush 5 ml + PPV)
- —- Lidocaine, Epinephrine, Atropine, Naloxone
ROSC + Cannot follow command > TTM (Targeted temp management)
# Foreign body obstruction
clinical : พูดไม่มีเสียง, ไม่มีเสียงไอ, เขียว > complete obstruction
- — มี conscious : Abdominal trusts (Heimlich) จนกว่าจะหลุด/partial
เด็กทารก ทำ Back slap, chest trusts
อ้วน/ตั้งครรภ์ ทำ chest trusts - — no conscious : chest compression (ไม่ต้องเช็ค pulse)
re-evaluate q 2 min (5 cycles)
[KNOWLEDGE]
Tachycardia with pulse (> 150/min in adult)
- ประเมิน ABC: O2 (ถ้า hypoxemic), Cardiac monitor, NIBP, O2 saturation
- ค้นหาและรักษาสาเหตุ **ดูว่า tachycardia เป็น primary หรือ secondary (ที่พบบ่อยคือ hypoxemia)
Unstable หรือไม่?: “BP drop ซึม Shock, AMI, Heart failure”
- Try adenosine 6 mg IV ได้ ถ้าไม่มี hypotension และเป็น regular narrow-complex SVT ระหว่างเตรียมทำ cardioversion
- Synchronized cardioversion (ถ้ามีเวลาควรให้ยา sedation)
- Narrow regular (SVT): 50-100 J
- Wide regular (VT): 100 J
- Narrow irregular (AF): 120-200 J (150 J)
- Wide irregular (VF): defibrillation dose
**ในกรณีที่จำเป็นต้องทำ cardioversion แต่ synchronize ไม่ได้ ให้ทำ unsynchronized shock (defibrillation dose) เช่นใน polymorphic VT
ถ้า stable ให้ทำ 12-lead EKG แล้วดูว่าเป็นตัวแคบ (QRS < 0.12s in adult, < 0.09s in pediatric) หรือตัวกว้าง (QRS > 0.12s)
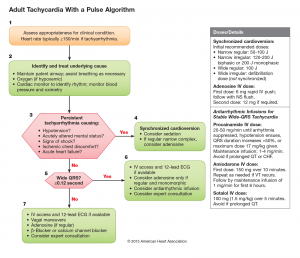 |
| Adult tachycardia AHA 2015 |
Adult: DDx SVT, VT, AF
- Narrow complex ได้แก่
- Sinus tachycardia (ไม่เกิน 220-อายุ) รักษาตามสาเหตุ
- SVT ได้แก่ atrial myocardium (atrial fibrillation), reentry circuit (PSVT: AVRT, AVnRT), autonomic tachycardia (ectopic atrial tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, MAT)
- Vagal manoeuvre, carotid sinus massage รักษาในกลุ่ม PSVT มีอัตราความสำเร็จ 25% ส่วนใน SVT กลุ่มอื่นๆอาจทำให้ ventricular rate ช้าลง ช่วยทำให้วินิจฉัยได้ง่ายขึ้น
- Adenosine 6 mg IV rapid push (antecubital vein) ตามด้วย NSS 20 mL flush ให้ซ้ำถ้าไม่ convert ใน 1-2 นาที ให้ adenosine 12 mg IV **ห้ามให้ใน asthma; ลด dose เหลือ 3 mg ในคนที่ใช้ dipyridamole, carbamazepine, heart transplant, หรือให้ทาง central line
- CCB/β-blocker สามารถ terminate PSVT และ slow ventricular response ของ SVT กลุ่มอื่นๆได้ ให้ diltiazem 15-20 mg (0.25 mg/kg) IV > 2 min ให้ซ้ำได้ในอีก 15 นาที 20-25 mg (0.35 mg/kg) แล้ว drip rate MT 5-15 mg/h
- Antiarrhythmic (amiodarone, procainamide, sotalol) สามารถใช้รักษาได้ แต่มี toxicity สูงจึงไม่แนะนำให้ใช้ ยกเว้นเป็น pre-excited atrial arrhythmia
**ให้เตรียม defibrillator พร้อมใช้ก่อนที่จะให้ยาที่กด AV node (adenosine, CCB, β-blocker) เพราะอาจเจอกับ pre-excited atrial fibrillation หรือ flutter (WFW) โดยบังเอิญได้
- Wide complex (regular)ได้แก่ VT, SVT with aberrancy, SVT with preexist block, pacemaker rhythm
-
- Try Adenosine สามารถรักษา PSVT ได้ แต่ไม่มีผลกับ VT
- Procainamide IV 20-50 mg/min จนกว่าจะ terminate, hypotension, QRS duration increase > 50%, max dose 17 mg/kg หลีกเลี่ยงใน prolonged QT, CHF
- Sotalol 1.5 mg/kg IV > 5 min หลีกเลี่ยงใน prolonged QT
- Amiodarone 150 mg IV > 10 min then drip 1 mg/min x 6h then 0.5 mg/min (max 2.2 gm/24h)
- Lidocaine 1-1.5 mg/kg IV bolus then drip 1-4 mg/min มีประสิทธิภาพต่ำที่สุด
- Irregular tachycardiaไม่ว่าจะเป็น narrow หรือ wide complex ส่วนใหญ่คือ atrial fibrillation +/- aberrant conduction (อื่นๆเช่น MAT, sinus rhythm with PAC)
-
- β-blocker/nondihydropyridine CCB (diltiazem) rate control
- Digoxin 4-6 mcg/kg IV > 5 min then 2-3 mcg/kg IV q 4-8 h หรือ amiodarone ในรายที่มี CHF
- ถ้าสงสัย pre-excited atrial fibrillation ให้ปรึกษาผู้เชี่ยวชาญ (ปกติ rate จะเร็วมากจนต้อง cardioversion ตั้งแต่แรกอยู่แล้ว)
- ถ้าเป็น polymorphic VT ให้ทำ defibrillation เมื่อกลับมาเป็น sinus rhythm ถ้ามี prolong QT ให้หยุดยาที่เป็นสาเหตุและแก้ไข electrolyte imbalance (Mg); ถ้าไม่มี prolong QT สาเหตุที่พบบ่อยสุดคือ AMI ให้ amiodarone หรือ β-blocker สามารถลดการเกิดซ้ำได้
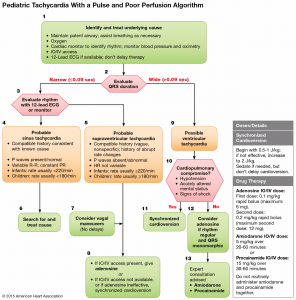 |
| Pediatric tachycardia AHA 2015 |
Pediatric: DDx SVT, VT
- Narrow complex (QRS < 0.09s)
- Sinus tachycardia (Hx มีสาเหตุกระตุ้น, P wave, ทารก < 220/min, เด็ก < 180/min)
- SVT (Hx เกิดขึ้นทันทีทันใด, abnormal P wave, HR ไม่เปลี่ยนแปลง, ทารก > 220/min, เด็ก > 180/min)
- พิจารณาทำ vagal manoeuvres (ทารก/เด็กเล็กให้วางน้ำแข็งที่หน้า; เด็กโตทำ carotid sinus massage/Valsalva manoeuvre-เป่าหลอดแคบๆ-)
- Adenosine 0.1 mg/kg IV (max 6 mg) 2 syringes technique โดย flush NSS 5 mL ตาม repeat 0.2 mg/kg IV (max 12 mg)
- Synchronized cardioversion 0.5-1 J/kg then 2 J/kg (sedation ถ้ามีเวลา)
- ถ้าไม่สำเร็จหรือเป็นซ้ำหลังจาก shock 2 ครั้ง พิจารณาให้ amiodarone 5 mg/kg IV > 20-60 min หรือ procainamide 15 mg/kg IV > 30-60 min
2. Wide complex (QRS > 0.09s)
- VT ให้ปรึกษาผู้เชี่ยวชาญก่อนการรักษาในเด็กที่อาการคงที่
- Synchronized cardioversion 0.5-1 J/kg then 2 J/kg (sedation ถ้ามีเวลา)
- Amiodarone 5 mg/kg IV > 20-60 min หรือ procainamide 15 mg/kg IV > 30-60 min (หยุดให้ถ้า BP ลดลงหรือ QRS widen)
VT แยกจาก SVT with aberrancy ดังนี้
- AV Disso : AV dissociation, fusion beat, capture beat
- เริ่ม R-ไป ตาก : Initial R in aVR; Northwest axis (positive in aVR, negative in I, aVF)
- ชี้ Same : Concordant in precordial lead
- กว้าง 4-S 100-มี knot : QRS in precordial > 160 ms (nonspecific); R to S > 100 ms in precordial (Brugada’s sign); R to S มี notching ( Josephson’s sign)
- หูซ้าย : if RBBB morphology = RSR’ complexes with a taller left rabbit ear(most specific)
Bradycardia with pulse
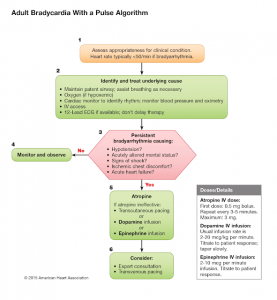
Bradycardia with pulse (< 50/min in adult)
- ประเมิน ABC: O2 (ถ้า hypoxemic), Cardiac monitor, NIBP, O2 saturation, IV access, 12-lead EKG
- ค้นหาและรักษาสาเหตุ **ที่พบบ่อยคือ hypoxemia
- Unstable หรือไม่?: “BP drop ซึม Shock, AMI, Heart failure”
- Atropine 0.5 mg IV repeat q 3-5 min (max 3 mg) มักจะไม่ได้ผลใน type II second-degree, third-degree AV block และใน cardiac transplant
- Dopamine IV 2-20 mcg/kg/min (dopamine (2:1) 3-30 ml/hr)
- Epinephrine IV 2-10 mcg/min (epinephrine (4:250) 7.5-37 ml/h) โดยเฉพาะถ้ามี hypotension
- Transcutaneous pacing (ตั้ง rate เริ่มต้นที่ 60 bpm, ปรับ output ให้สูงกว่าระดับที่เห็น ECG captured 2 mA, และประเมิน circulation โดยการคลำ femoral pulse [TCP ทำให้ muscular movement คล้าย carotid pulse ได้])
- Consult expert/Transvenous pacing
 |
| adult bradycardia AHA 2015 |
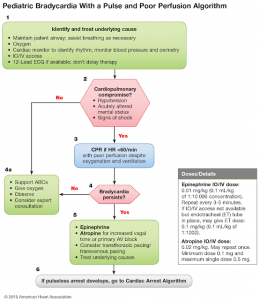
**ในเด็กหลังจากให้ O2 & ventilation แล้วยังมี poor perfusion ให้ทำ CPR โดยให้ epinephrine (1:10,000) 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg) q 3-5 min; ถ้าเกิดจาก increased vagal tone ให้ atropine 0.02 mg/kg (min 0.1 mg, max 0.5 mg); ถ้าเป็น complete heart block หรือไม่ตอบสนองต่อการรักษาอื่นๆให้รีบทำ transcutaneous pacing
 |
| Pediatric bradycardia AHA 2015 |